Here's a dead simple guide to understanding it:
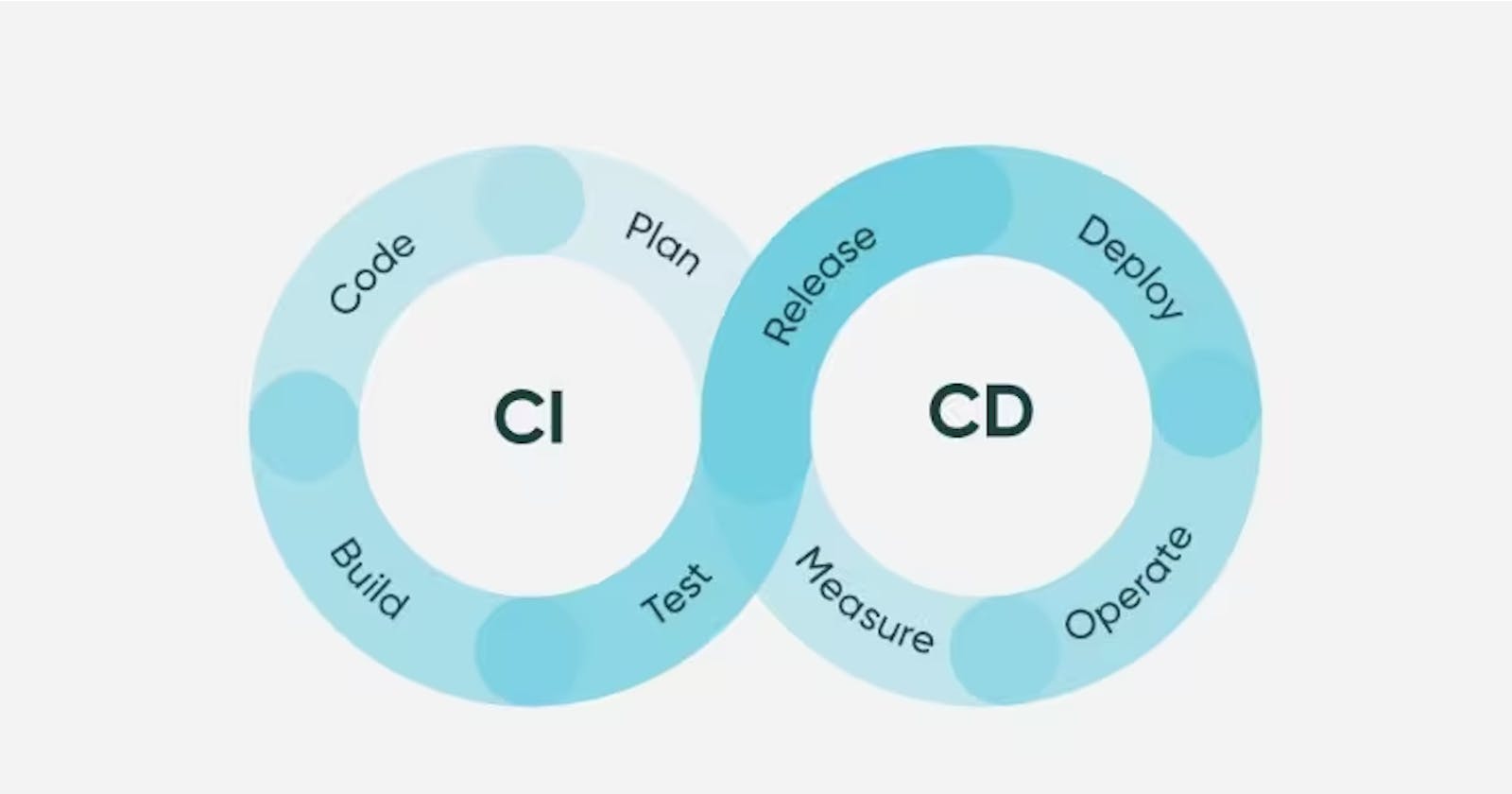
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment.
It's a process where code changes are regularly merged into a shared repository, and then automatically deployed to a staging or production environment.
Continuous Integration (CI) refers to the process where code changes are merged regularly and frequently.
By pushing small changes at a higher frequency, teams can catch and fix problems early, keeping the codebase stable and up to date.
Continuous Deployment (CD) automates the process of deploying changes to a staging or prod environment as soon as they are merged in.
This can save a lot of time and effort that would otherwise be spent manually deploying changes, or waiting for scheduled tasks to do it.
A comprehensive CI/CD pipeline can be used to build, test, and deploy changes automatically while alerting you about any problems.
This setup requires various tools, such as version control software like Git, container management tools like Docker and Kubernetes, and automation tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Argo CD, Terraform, and Ansible.
A CI/CD pipeline streamlines the development process by automating manual processes and reporting on problems early.
It also removes the potential for human error that can occur with manual testing and deployment.
Why do DevOps Engineers need to know CI/CD?
A DevOps team is responsible for automating and streamlining processes, which a CI/CD pipeline accomplishes.
They play a vital role in building and maintaining CI/CD pipelines and are usually the ones leading the effort.
I write about DevOps and Cloud computing-related blogs make sure to check out my other blogs and feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn.
If you run an organization and want me to write about anything please do connect with me 🤝.